Can a car accident cause whiplash?
The short answer is absolutely! There are millions of car accidents in our country every year and here in St. George, UT there are hundreds of potential whiplash injuries every month. Many of these car accidents will result in whiplash injuries, but that is not all! There are so many varying injuries that result from car crashes that are difficult to include them all in one article. We begin by discussing whiplash, and from there, branch out into other types of car crash injuries that we see most frequently here in our office. My primary focus will be spinal disc injuries and facet joint injuries.
What is whiplash?
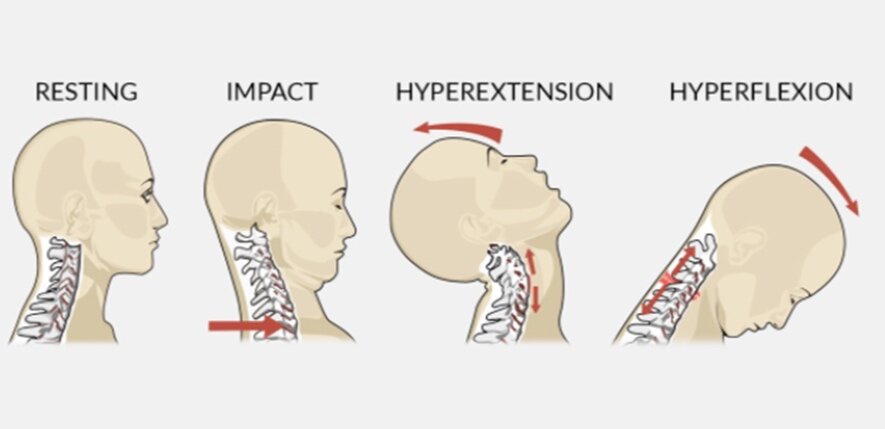
Have you ever seen a cowboy crack a whip? The rapid back and forth forceful whipping of a flexible cord with the force being applied to one end (the fixed end) results in a greater force of the action at the loose end (or unfixed end). To really slow down the action in the case of a rear-end car accident collision, imagine a person sitting still when suddenly another vehicle from behind smashes into the back of their car. This impact will certainly send the vehicle that was hit in a sudden forward motion which, in effect will then cause the occupants of the car to also suddenly move forward. Now, as you can imagine, any part of the body that is not fixed to something within the vehicle such as a person’s back fixed to the seat, will not move forward with the body. So as the body and vehicle move forward suddenly, the head remains stationary while the body explodes forward. This results in overstretch of all connective tissues within the neck. The initial effect is strain injury to the front of the neck because as the body moves forward, the head moves backward, and the stretch happens in that region. The next motion is what is truly referred to as the “whiplash” as the head comes forward with greater momentum and force than the original impact. As the head whips past the body, there is an accelerated overstretch of the back of the neck damaging those connective tissues as well. The initial injury of whiplash, or cervical spine acceleration-deceleration injury, mostly affects the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the neck and upper back.
Whiplash injuries are most frequently caused by rear-end car accidents. While most of these whiplash cases will get better within a few weeks, some people have chronic neck or other spine pains with long-lasting complications for a lifetime. We feel it is important to mitigate the long-term effects of whiplash by treating in a manner that full healing occurs. Unfortunately, many doctors and patients follow the “watch and wait” methodology, which in my opinion, is very dangerous and sometimes irresponsible. When you look at the tissues that are injured in a whiplash case, primarily muscles tendons, and ligaments, under a microscope, you will see that there is tearing that occurs in a lot of the cellular structures of these connective tissues. This tearing takes time to heal. But many times, the healing is with scar tissue. The more aggressive the injury or deeper the tearing, the greater the potential for scar tissue build-up. Scar tissue is not nearly as flexible or strong as the original muscles, tendons, and ligaments that may be injured. During the initial stages of healing, scar tissue doesn’t seem to be a problem because the damage is being stabilized. As time goes on, however, the person will notice stiffness and soreness especially in the mornings, loss of range of motion of the neck which manifests as the inability to turn their head fully, soreness with normal movements, headaches, and a myriad of other movement disorders that can be an aggravation in day-to-day life. Many times these effects from the automobile accident and subsequent whiplash injury go undetected because they still feel like they are simply going through the normal healing stages following the original injury. Many times it is not until months (and occasionally, years) before a person starts to recognize that this is not normal healing. It is vitally important to be under the care of a healthcare practitioner who is well-versed in treating post-car accident injuries.
Can whiplash cause spinal disc bulges?
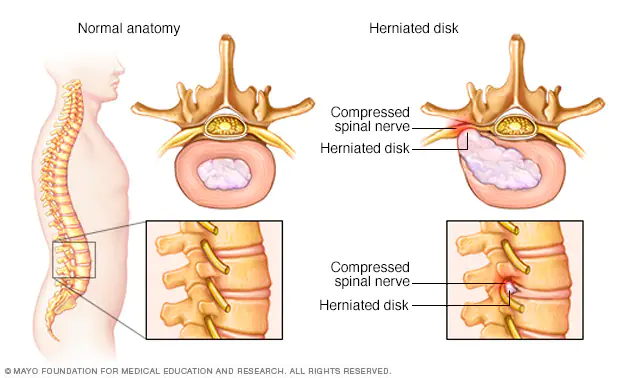
Spinal discs are the cushions that reside between the vertebrae of the spine. There are 23 discs in the entire spine comprised of the neck, mid-back, and low back or cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines. As you read above, the whiplash effect of the neck as accelerated forward and backward motion also has the potential of causing compression on either the front or the back of the spine during this same whipping motion. Factors such as seated posture, body or head rotation, the tilt of the seat, the direction of a car crash or impact, vehicle speed, and subsequent G forces, all play a role in the damage to the body. Naturally, the greater the difference of speed between the vehicle the injured person is riding in and whatever object they collide with, whether it be another vehicle or stationary object, results in greater injury potential.
Spinal or intervertebral, discs bear much of the compression load that the spine experiences not only do the forces of gravity but due to the position of the vertebra during compression. Also, during a whiplash injury, there are shearing forces that occur as each segment of the spine is being whipped forward and backward. Spinal discs are tough collagen-based tissues that, when damaged, can swell, inflame and rupture. These are diagnosed as bulging, herniated, or protruding disc injuries. Spinal disc bulges, herniations, and protrusions are most of the reasons for spinal surgeries. Left untreated, disc injuries can result in accelerated degeneration of the spine, radiating nerve pains, even partial paralysis! Therefore it is extremely critical that therapeutic intervention is used early in a whiplash case in order to mitigate the potential damage and to have a chance at avoiding surgery later on.
The good news regarding spinal disc care is that there are many natural, safe, and effective ways to treat and avoid surgery. The primary methodology used in my practice is spinal decompression coupled with laser therapy to promote healing in bulging, herniated, and protruding discs. Spinal decompression is a wonderful name for the therapy that we do as it’s very descriptive of what we’re trying to accomplish. With the patient in a prone position, we are able to use simple belts and gentle pulling methods in order to help with spine and disc alignment which aids in proper healing, position, and movement restored to the spine. The pain relief is amazing! Decompression therapy is very pleasant throughout the entire treatment. There is an old adage that says, “No pain, no gain!”…this certainly does not apply here! Patients who are treated with spinal decompression therapy and our therapeutic laser treatments are pleasantly surprised by how comfortable the treatment is and how quickly they get better even when they have had pain for many months.
Do Car Accidents Cause Facet Syndrome?
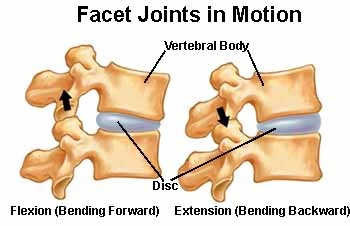
Facet syndrome (aka Dorsopathy) is a condition where the facet joints of the spine become inflamed and irritated. In the case of an auto accident injury stemming from a car crash, the facet joints which are primarily used for assisting directional movements of the spine can become inflamed and irritated as they are overstretched and compressed during the whiplash injury. For similar reasons, to the intervertebral discs and other connective tissues, the facet joints become injured also by compression during the acceleration part of the whiplash and overstretch during the deceleration part of the whiplash effect from the car accident. These joints are comprised of a joint capsule surrounding the two cartilage surfaces that are intended to glide on each other during normal movement. In the case of overstretching or compression, as in an acceleration/deceleration injury, the joint capsule can become torn, and/or the cartilage can become compressed or bruised. The pain that stems from a facet joint injury can be very debilitating causing great difficulty in normal activities such as sleeping, turning the head, looking up or down,… i.e. most neck movements.
Again, the best treatment for facet joint injuries whether they be sprain/strain type, whiplash, or chronic dorsopathy, is to restore normal joint movements and freedom of full range of motion. There is a myriad of ways to treat facet joint problems in the case of car crash injuries. When more acute, facet joints respond well to anti-inflammatory medications, soft tissue manipulation, ultrasound therapy, laser therapy, spinal decompression, electrical muscle stimulation, and cryotherapy (ice). After the initial swelling and inflammation begin to calm down, then more aggressive means of restoring joint motion may be applied such as chiropractic manipulation, range of motion exercises, and return to full activities of daily living including work and exercise activity.
Do car accidents cause nerve damage?
Nerve damage can be felt when there is severe damage and inflammation to the connective tissues (muscles, tendons, and ligaments), intervertebral discs, and facet joints. In the case of a severe whiplash injury, there can actually be damage to the nerves themselves as well. Nerves are part of what I like to refer to as “free-hanging electrical wiring” that controls all systems and sensations in the body. The nerves originating in the brain passed down through the spinal canal branching off at every level of the spine and supplying the entire body with much-needed information and sensations. Nerve cells are very delicate but are housed inside of a very tough sheath, known as a myelin sheath, to protect them. When this myelin sheath becomes overstretched, partially torn, or compressed, this can cause severe radiating pain, numbness or tingling, and or weakness affecting the area of the body that it supplies. It’s rare that a nerve will be damaged in the case of the whiplash injury without other tissues being involved as well. Nerves travel everywhere in the body surrounding and passing between all joints, muscles, connective tissues, and even skin. Nerves not only carry pain signals that are supplying those tissues when they are injured but also can become part of the injury itself when those tissues and their associated inflammation from injury will cause nerve compression resulting in an increase of localized pain or numbness and tingling that may radiate to the extremities. The good news is that tissues in the body have a tendency to heal so long as the environment for that healing is optimal. This means that inflammation needs to be reduced quickly, normal joint motion restored, and scar tissue prevented. While all three of these are extremely imperative to correct, it is important to understand that inflammation and loss of normal joint motion are the two problems that result in scar tissue formation. In other words, if we reduce inflammation and restore normal joint motion, that is the way that scar tissue is most likely prevented in the case of a car accident resulting in whiplash.
As the nerves exit the spine in their individual branches, they pass by the intervertebral discs, facet joints, various muscles, tendons, and ligaments. In the case of a severe whiplash injury, there can be tissue damage associated with all of the structures. So if the intervertebral disc is bulged and swollen, the facet joint has some tearing along with the various muscles, tendons, and ligaments, the result can be a painful situation where the nerve endings connected with each of these tissues are sending their respective pain signals to the brain. Along with this, however, the nerves themselves may be impinged upon by those swollen damaged tissues resulting in additional numbness, tingling, or even partial paralysis (manifested as weakness of a muscle or group of muscles) to the body region that those nerves supply. This is why it is very common to see individuals with neck pain and stiffness following an accident accompanied by numbness and tingling radiating all the way down the arm and into the fingers within days or weeks following a car accident or other motor vehicle crash.
What are the best treatments for whiplash injuries?
As we have discussed above, in a severe whiplash injury, the three (well actually four) primary tissues involved in whiplash cases are:
- Connective tissues (Muscles, tendons, and ligaments) manifesting as sprain or strain injuries.
- Intervertebral Discs manifesting as disc bulges, herniations, and protrusions.
- Facet joints manifesting as Dorsopathy or capsular sprain.
- Nerves manifesting as radiating pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness.
While each of these types of conditions requires slight variation in how we manage them, in the initial stages the goal is to reduce inflammation and help in aiding normal joint motion. Within the first 48 hours following a car crash, it is imperative to start therapies that will reduce the inflammation such as ultrasound therapy, cryotherapy (ice), trigger point injections, gentle soft tissue manipulation or massage, electrical muscle stimulation, and anti-inflammatories. The goal within the first two weeks following a car accident is to significantly reduce the range of motion and pain. Once 25 to 50% of the initial pain is alleviated, the more specific and serious causes of the pain will begin to manifest. In other words, when someone is so stiff and sore after a serious auto accident, many times it’s very difficult to assess where most of their pain is emanating from because it hurts to do just about every movement. Even with an MRI or x-rays, it may sometimes be difficult to tell exactly what tissues are causing the most pain and limitations during the early stages of treatment. Therefore after pain has reduced 25 to 50%, we perform orthopedic maneuvers that help diagnose which tissues sustain the brunt of the injury. Depending on which type of tissue is worst will determine which therapies we will proceed with, moving forward. If it’s primarily connective tissue damage, then we would proceed with gentle chiropractic manipulation, mechanical traction, trigger point injections, and continued ultrasound therapy. If the intervertebral discs have sustained most of the damage and manifest as a bulged disc or herniated disc, then the treatment option would likely include spinal decompression and laser therapy. When facet joints are the primary injured area, chiropractic manipulation, heat, deep myofascial massage, and trigger point injections are preferred. When the nerves are damaged, they respond best to the above treatments for whatever tissue might be causing the secondary nerve symptoms. In the case of primary nerve symptoms, rest, ice, and heat contrast over the symptomatic area, ultrasound therapy, laser therapy, and gentle joint mobilization will go a long way in helping restore a better healing environment for those tissues. When there is primary nerve damage, we treat the same as is shown above but also may refer to a pain management specialist for additional medical intervention which may include prescription anti-inflammatories, muscle relaxants, and/or neuro-statins.
The bottom line is that when you have been injured in a car crash or some kind of automobile accident it is extremely important to seek care early in order to get a proper whiplash diagnosis, an indication of how extensive the injuries are, and begin an appropriate treatment protocol that will yield the best results for your specific case and injuries.